Pipelines for merge requests (FREE)
You can configure your pipeline to run every time you commit changes to a branch. This type of pipeline is called a branch pipeline.
Alternatively, you can configure your pipeline to run every time you make changes to the source branch for a merge request. This type of pipeline is called a pipeline for merge requests.
Branch pipelines:
- Run when you push a new commit to a branch.
- Are the default type of pipeline.
- Have access to some predefined variables.
- Have access to protected variables.
Pipelines for merge requests:
- Run when you:
- Create a new merge request.
- Push a new commit to the source branch for a merge request.
- Select Run pipeline from the Pipelines tab in a merge request. This option is only available when pipelines for merge requests are configured for the pipeline.
- Do not run by default. The jobs in the CI/CD configuration file must be configured to run in pipelines for merge request.
- Have access to more predefined variables.
- Do not have access to protected variables.
Both of these types of pipelines can appear on the Pipelines tab of a merge request.
Types of pipelines for merge requests
The three types of pipelines for merge requests are:
- Pipelines for merge requests, which run on the changes in the merge request's
source branch. These pipelines display a
detachedlabel to indicate that the pipeline ran only on the contents of the source branch, ignoring the target branch. - Pipelines for merged results, which run on the result of combining the source branch's changes with the target branch.
- Merge trains, which run when merging multiple merge requests at the same time. The changes from each merge request are combined into the target branch with the changes in the earlier enqueued merge requests, to ensure they all work together.
Prerequisites
To use pipelines for merge requests:
- Your project's CI/CD configuration file must be configured with jobs that run in pipelines for merge requests. To do this, you can use:
- You must have at least the Developer role in the source project to run a pipeline for merge requests.
- Your repository must be a GitLab repository, not an external repository.
Use rules to add jobs
You can use the rules keyword to configure jobs to run in
pipelines for merge requests. For example:
job1:
script:
- echo "This job runs in pipelines for merge requests"
rules:
- if: $CI_PIPELINE_SOURCE == 'merge_request_event'You can also use the workflow: rules keyword
to configure the entire pipeline to run in pipelines for merge requests. For example:
workflow:
rules:
- if: $CI_PIPELINE_SOURCE == 'merge_request_event'
job1:
script:
- echo "This job runs in pipelines for merge requests"
job2:
script:
- echo "This job also runs in pipelines for merge requests"
Use only to add jobs
You can use the only keyword with merge_requests
to configure jobs to run in pipelines for merge requests.
job1:
script:
- echo "This job runs in pipelines for merge requests"
only:
- merge_requestsUse with forked projects
- Introduced in GitLab 13.3.
- Moved to GitLab Premium in 13.9.
External contributors who work in forks can't create pipelines in the parent project.
A merge request from a fork that is submitted to the parent project triggers a pipeline that:
- Is created and runs in the fork (source) project, not the parent (target) project.
- Uses the fork project's CI/CD configuration, resources, and project CI/CD variables.
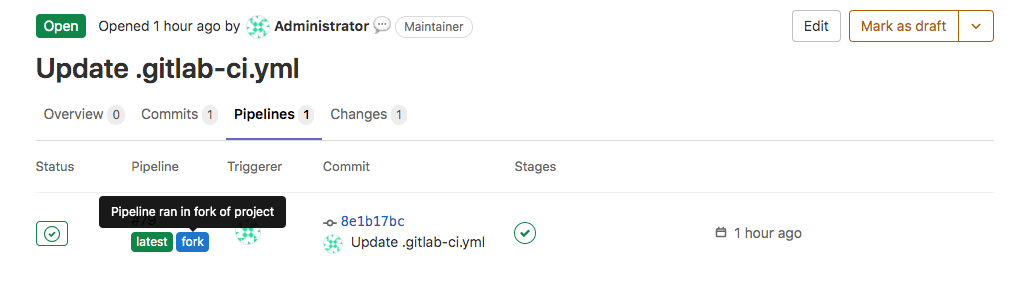
Pipelines for forks display with the fork badge in the parent project:
Run pipelines in the parent project (PREMIUM)
Project members in the parent project can choose to run a pipeline for merge requests for a merge request submitted from a fork project. This pipeline:
- Is created and runs in the parent (target) project, not the fork (source) project.
- Uses the CI/CD configuration present in the fork project's branch
- Uses the parent project's CI/CD configuration, resources, and project CI/CD variables.
- Uses the permissions of the parent project member that triggers the pipeline.
Run pipelines in fork project MRs to ensure that the post-merge pipeline passes in the parent project. Additionally, if you do not trust the fork project's runner, running the pipeline in the parent project uses the parent project's trusted runners.
WARNING: Fork merge requests can contain malicious code that tries to steal secrets in the parent project when the pipeline runs, even before merge. As a reviewer, carefully check the changes in the merge request before triggering the pipeline. GitLab shows a warning that you must accept before you can trigger the pipeline.
Parent project members with at least the Developer role can create pipelines in the parent project for merge requests from a forked project:
- In the merge request, go to the Pipelines tab.
- Select Run pipeline. You must accept the warning, or the pipeline does not run.
Available predefined variables
When you use pipelines for merge requests, you can use:
- All the same predefined variables that are available in branch pipelines.
- Additional predefined variables available only to jobs in pipelines for merge requests. These variables contain information from the associated merge request, which can be when calling the GitLab Merge Request API endpoint from a job.
Troubleshooting
Two pipelines when pushing to a branch
If you get duplicate pipelines in merge requests, your pipeline might be configured to run for both branches and merge requests at the same time. Adjust your pipeline configuration to avoid duplicate pipelines.
In GitLab 13.7 and later,
you can add workflow:rules to switch from branch pipelines to pipelines for merge requests.
After a merge request is open on the branch, the pipeline switches to a merge request pipeline.
Two pipelines when pushing an invalid CI/CD configuration file
If you push an invalid CI/CD configuration to a merge request's branch, two failed pipelines appear in the pipelines tab. One pipeline is a failed branch pipeline, the other is a failed pipeline for merge requests.
When the configuration syntax is fixed, no further failed pipelines should appear. To find and fix the configuration problem, you can use:
- The pipeline editor.
- The CI lint tool.
The merge request's pipeline is marked as failed but the latest pipeline succeeded
It's possible to have both branch pipelines and pipelines for merge requests in the Pipelines tab of a single merge request. This might be by configuration, or by accident.
If both types of pipelines are in one merge request, the merge request's pipeline is not considered successful if:
- The branch pipeline succeeds.
- The pipeline for merge request fails.
When using the merge when pipeline succeeds feature and both pipelines types are present, the pipelines for merge requests are checked, not the branch pipelines.